First, the thread is stressed
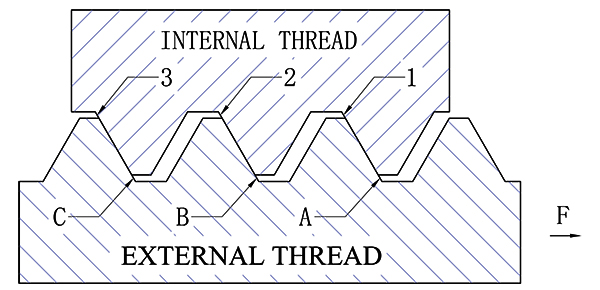
The nut is matched with the bolt, the pitch is equal, the first turn of the nut thread 1 side stretches under the action of preload, the length between the A side of the bolt thread and the B side is also stretched, and the force generated by the thread stretch acts on the 2 sides of the second circle of the nut thread through the B side of the bolt thread. Because the stress area of the bolt is less than the stress area of the hexagon nut, the force of the bolt thread is less than the force of the nut thread when the same tensile deformation length is smaller, so the force on the first side of the nut thread is greater than the force on the second side of the nut thread, and the force on the A side of the bolt thread is greater than the force on the B side of the bolt thread. By analogy, the force on the 2nd side of the nut thread is greater than the force on the 3rd side of the nut thread, and the force on the B side of the bolt thread is greater than the force on the C side of the bolt thread.
According to the theoretical calculation, when the hexagon nut is used with the bolt, the average force of the first circle of the thread reaches about 30% of the total load, because the thread is continuous, the so-called first circle of the thread is only used for analysis and calculation, in fact, the force of each point on the thread is not the same, the maximum force is more than 40%, here it is easy to produce thread tripping and bolt stress excessive fracture.
Second, the principle of loosening
Nut loosening is an inevitable process under vibration, impact and other variable loads, first loosen and then move; Loosening is the reduction of the residual preload, when the tightening moment formed by the residual preload is less than the instantaneous loosening trend of the nut, the nut rotates and loosens. The conventional nut preload is too small to ensure the residual preload, and when the thread force exceeds the yield strength of the material, the plastic deformation is generated, and the residual preload can not be guaranteed, which is the fundamental reason why the conventional nut is not loosened.
When the thread is plastically deformed under variable load, the force on each circle of thread is continuously redistributed, and the preload is gradually reduced until the thread no longer produces plastic deformation.
Third, principle of anti-pine for regular use
In order to prevent the plastic deformation of the thread, most of them reduce the initial preload and then prevent the nut from rotating to achieve anti-loosening. In this kind of anti-loosening structure, the smaller the initial preload, the greater the ratio of the residual preload to the initial preload, the better the anti-loosening effect, and the evaluation criteria of the two test methods that meet the requirements of "GB/T 10431-2008 Test Method for Transverse Vibration of Fasteners" or "ISO 16130-2015-08 Aerospace Series - Dynamic Test of Locking Performance of Bolted Joints under Transverse Loading Conditions".
The reduction of the initial preload causes the lack of rigidity of the threaded connection, and the bolt is easy to fatigue break, which is also the main reason for the failure of the bolt.
Affected by the uneven force of the thread, the current commonly used locknut or locknut structure usually has an initial preload of about 50% of the guaranteed load of the bolt, and the maximum working load is less than the yield strength of the thread, that is: residual preload + working load ≦ load when the thread is plastically deformed (the hexagon nut series generally does not exceed 75% of the guaranteed load of the bolt).